1. [Process]
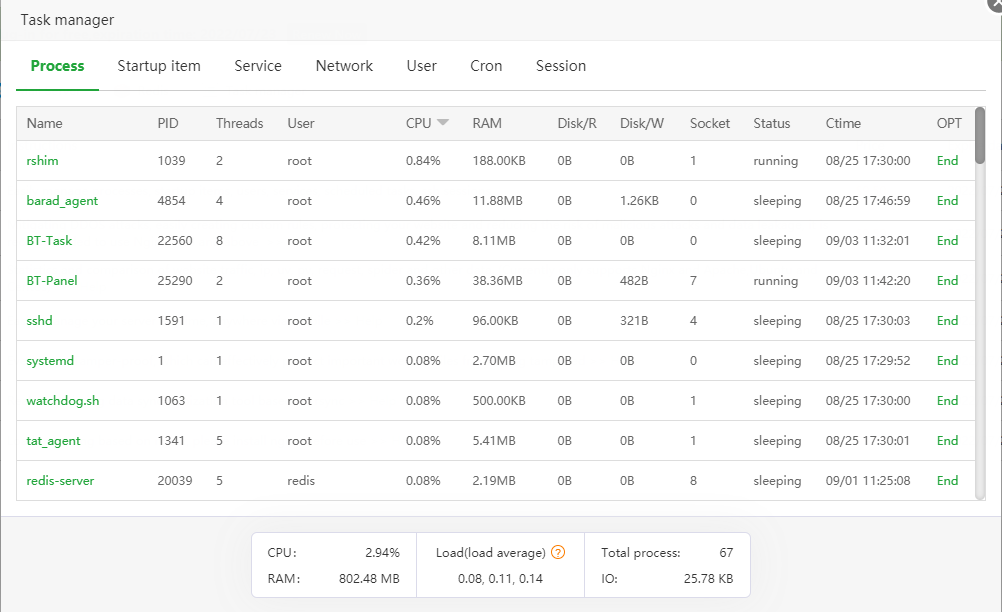
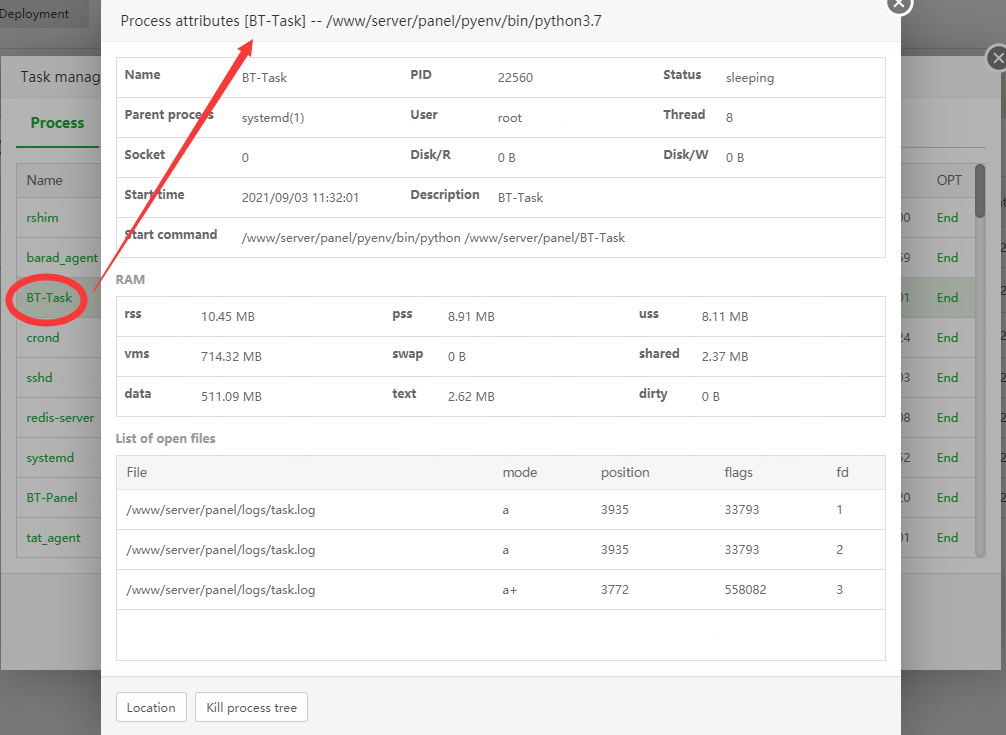
Describe:
Track the CPU/memory/disk usage of each process, click on the process name to view more detailed information about the process
Sort:
By default, in descending order of CPU usage, users can click on the header of each column to sort
Glossary:
Disk/R | Disk/W: the speed at which the process reads and writes to the disk per second
vss: memory allocated but not actually used (including memory occupied by shared libraries)
rss: Actual physical memory used (including memory occupied by shared libraries)
pss: physical memory actually used (proportional allocation of memory occupied by shared libraries)
uss: physical memory occupied by the process alone (not including memory shared across processes)
swap: The size of the swap area (virtual memory) occupied by the process
Load average: Display the average load of the system for 1 minute, 5 minutes, and 15 minutes
End the process tree:
End all child processes
Recursively terminate all parent processes except for critical system processes
End all processes with the same name
List of open files:
All files that have been opened by the current process
2. [Startup item]
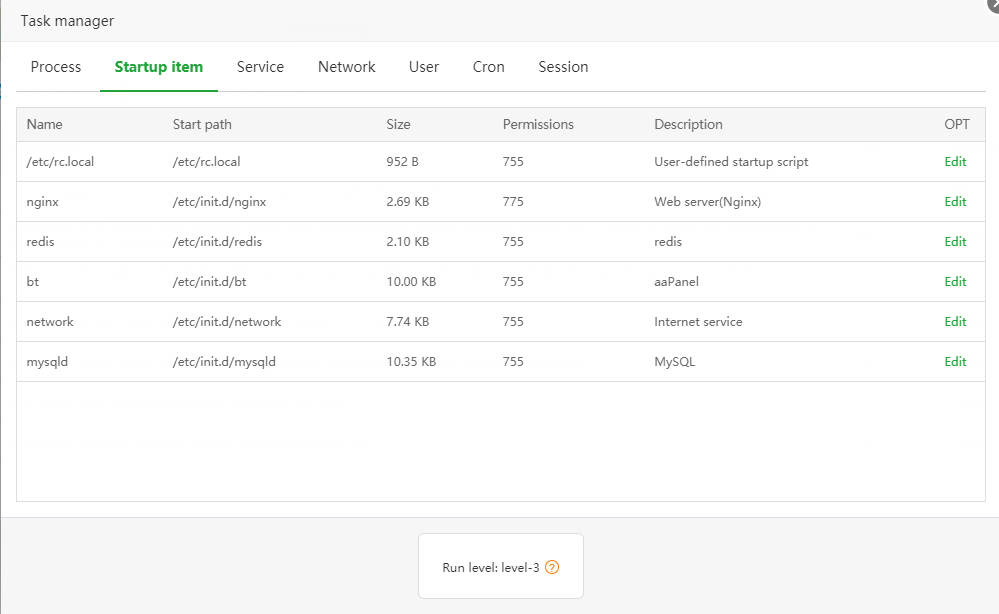
Describe:
List all items started with the system, including init service, user-defined startup script
Edit:
Through the online editor, you can view or modify all startup scripts, which is convenient for users to quickly find and exclude malicious scripts
3. [Service]
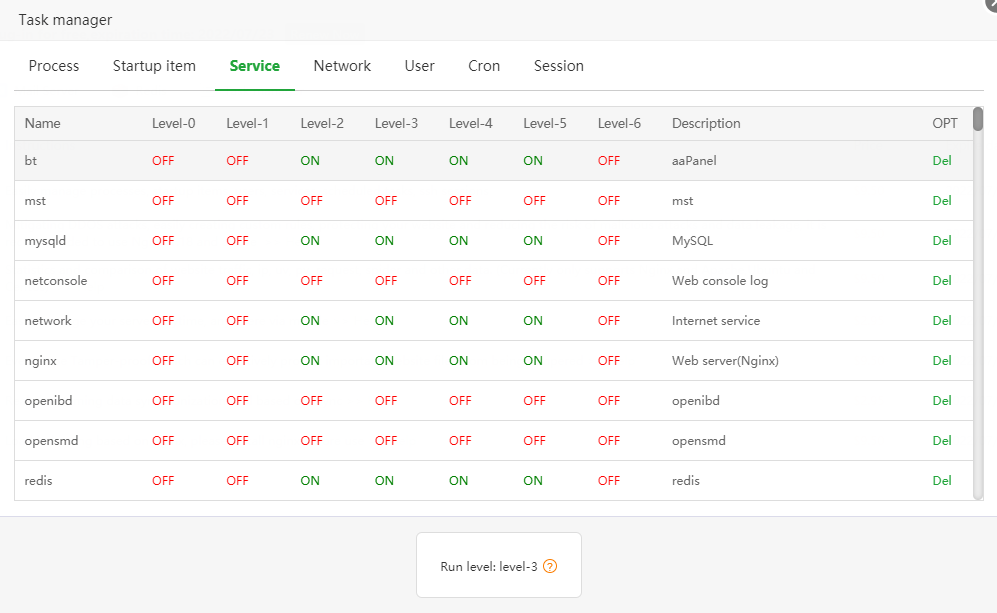
Run level:
Each service has a corresponding run level setting. If the corresponding run level is set to open, it means that the system will start the service at the corresponding run level. The status of each run level is listed below
Level-0: Shut down
Level-1: Single user mode
Level-2: Multi-user mode without network
Level-3: Full multi-user mode in command line mode (the server usually runs in this mode)
Level-4: The system is not used
Level-5: Graphical GUI mode (some systems with GUI installed will automatically enter this mode)
Level-6: Restart
Delete service:
The panel first tries to use the stop command to stop the service, and then delete the service
Note: It is not currently supported to directly delete the services hosted by Systemctl
Set the run level status:
You can set whether each service is started at the specified run level, and the services managed by Systemctl only support setting the status of the current run level of the system.
Warning: Please do not arbitrarily modify the run level status of system services, and do not easily assign third-party services to Level-0 or Level-6 run levels. This may cause your system to fail to start normally.
4. [Network]
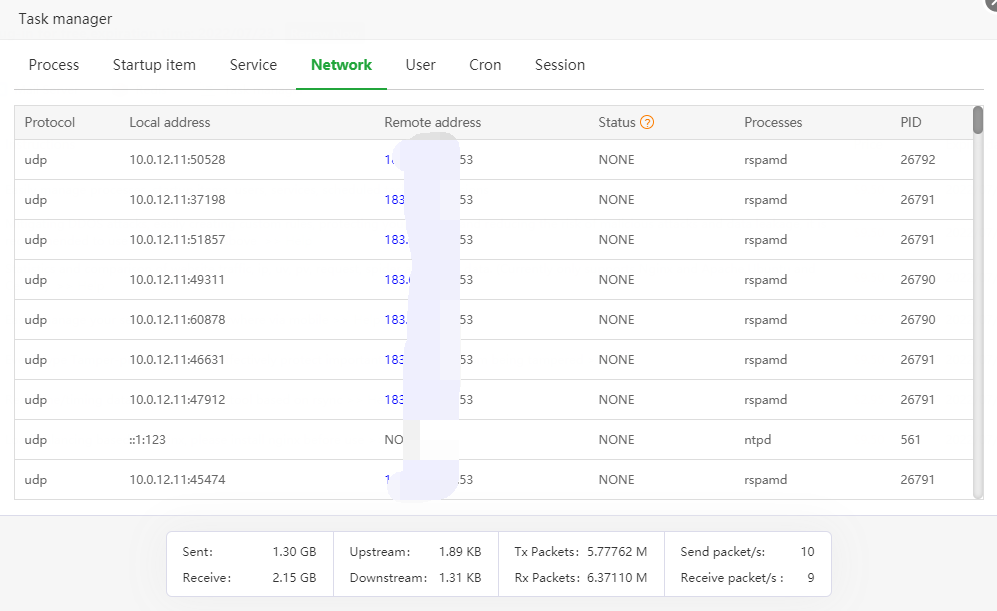
Describe:
Quickly view the current server network status
State name explanation:
LISTEN: monitor status, waiting for user connection
TIME_WAIT: The server actively closes the connection and will automatically release resources after 3 times the connection life cycle
CLOSE_WAIT: The client actively closes the connection and waits for the server to release resources
ESTABLISHED: The connection that is communicating normally
NONE: UDP connection
5. [User]
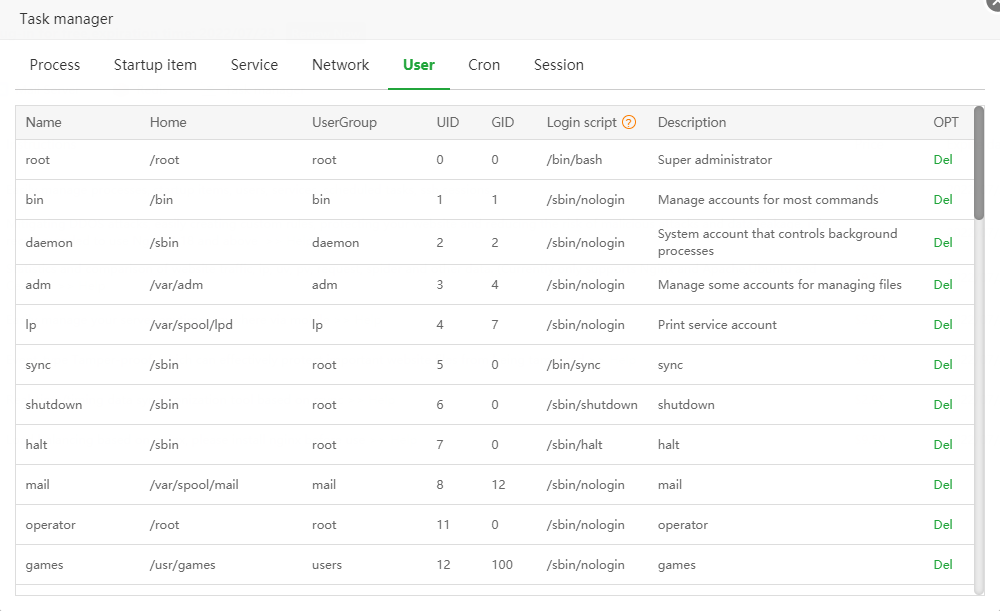
Glossary:
home: the user's home directory
uid: the unique identifier of the user in the Linux system
gid: the unique identifier of the user group in the Linux system
Login script:
The script that runs when the user logs in to the system
/bin/bash: After logging in, process the bash command line
/sbin/nologin: Login is prohibited
/bin/false: Login is forbidden, and the use of any services is also forbidden
/sbin/shutdown: shutdown script
Other: Custom script
Delete users:
The program will try to delete the user. If it detects that a process is using the user, it will end the process before deleting it.
Note: By deleting the user here, the program will end all the processes using the user without dying until the user is successfully deleted
Warning: Deleting a user arbitrarily will cause the software that depends on the user to be abnormal, please operate with caution
6. [Cron]
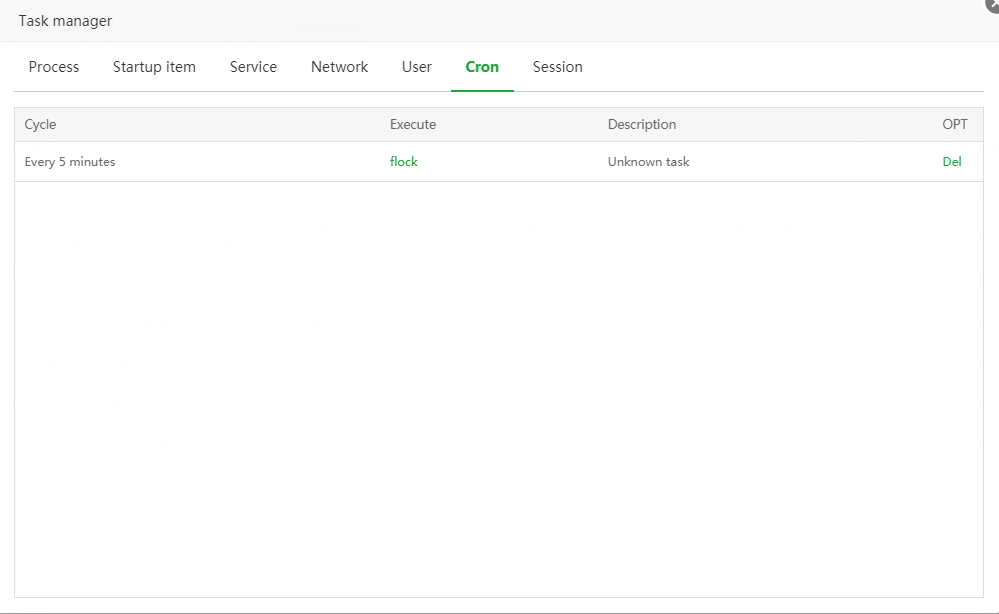
Describe:
Analyze all scheduled tasks in the crond service, users can view the task cycle, content, or delete the specified task
7. [Session]
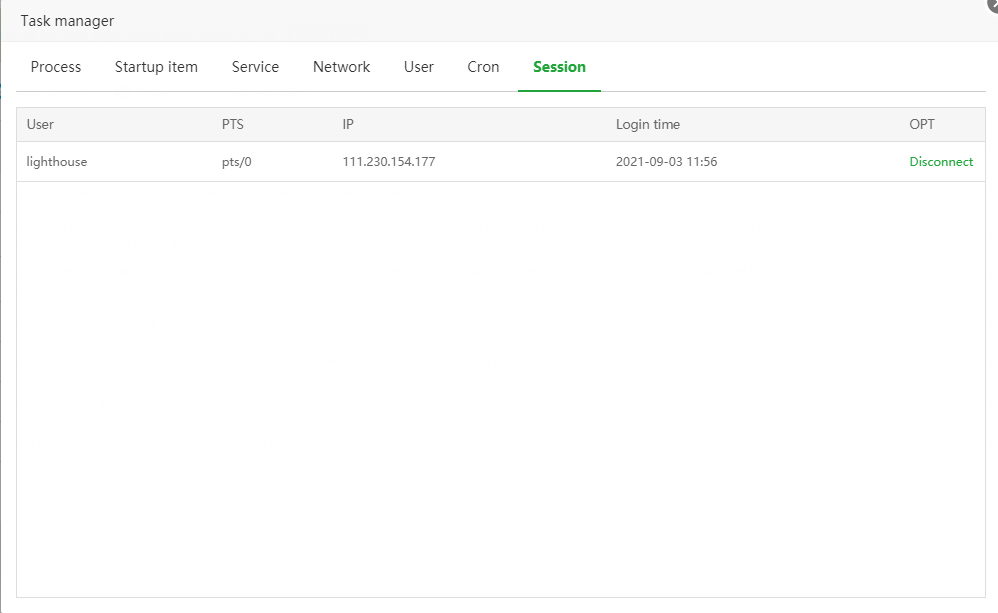
Describe:
List the current sessions that have successfully logged in to the system via SSH
Disconnect:
Directly forcibly interrupt the specified session
Warning: Forcibly interrupting the session will also interrupt the operation being performed in the session, please operate with caution